Explain the Differences Between Stationary and Mobile Phases
If mobile phase is liquid it is termed as liquid chromatography LC and if it is gas then it is called gas chromatography GC. The components of the analyte interact differently with these ytwo phases.

Difference Between Stationary And Mobile Phase Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms
Most of the times scientists use an aqueous blend of water with a miscible polar organic solvent such as acetonitrile or methanol as the mobile phase.
. The stationary phase is a matrix of porous polymer which have pores of specific sizes. Subtle differences in a compounds partition coefficient result in differential retention on the stationary phase and thus affect the separation. Other Apps - April 15 2022 Principle Instrumentation Various Parameters And Applications Of Hplc.
Reverse phase chromatography is one where the stationary phase is less polar and the mobile phase is polar. The stationary phase remains fixed in place while the mobile phase carries the components of the mixture through the medium being used. The stationary phase acts as a constraint on many of the components in a mixture slowing them down to move slower than the mobile phase.
Therefore the analytes interact with the nonpolar stationary phase. When the sample is injected with the mobile phase the mobile phase occupies the pores of the stationary phase. In planar chromatography the stationary phase is short.
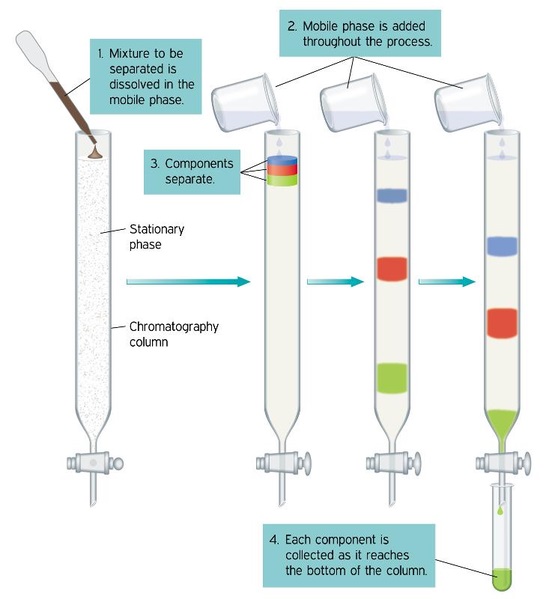
One of these phases in the form of a porous bed bulk liquid layer or film is generally immobile stationary phase while the other is a fluid mobile phase that. Chromatography is essentially a physical method of separation in which the components of a mixture are separated by their distribution between two phases. Stationary phase in chromatography is a solid phase or a liquid phase coated on the surface of a solid phase.
The observations made on the C18 phase were compared on three additional stationary phases ie. Gas chromatography requires very high temperatures to work and is generally performed in a tube. It is a process of separation of components of a mixture based on the relative differences in adsorption.
The mobile phase is the moving phase and the stationary phase is the nonmoving phase in a chromatographic separation. In gas chromatography the components of a sample are dissolved in a solvent and vaporized in order to separate the analytes by distributing the sample between two phases. Alkyl amide fluorophenyl and biphenyl which had previously been shown to possess large selectivity differences towards these peptides on a limited sub-set of mobile phases.
Briefly explain the difference between stationary and mobile phases in column and planar chromatography. Briefly explain the difference between stationary and mobile phases in column and planar chromatography. Furthermore the stationary phase of the normal phase chromatography is mainly pure silica and the mobile phase is a non-aqueous solvent such as chloroform while the stationary phase of the reverse phase chromatography is a modified silica substrate with long hydrophobic long chains and the mobile phase is mainly water methanol or acetonitrile.
Planar chromatography rapidly separates the analytes. The mobile phase is often called an eluent or solvent that is pumped through the column filled with the stationary phase often at a specific flow rate. What Is The Difference.
To put it simply the mobile phase is the phase in chromatography where the solution being tested or separated is injected before it is passed through the stationary phase. In the context of gas chromatography the stationary phase often consists of an area densely packed with beads. If the stationary phase is polar in nature the polar component of the sample adsorbs to it while others move on.
Mobile phase flowing over the stationary phase is a gaseous or liquid phase. Explain the difference between the mobile phase and the stationary phase and list what is used for mobile phases versus stationary phases for thin-layer chromatography and column chromatography. Column chromatography requires a less polar mobile phase compared to the planar chromatography.
Explain the Differences Between Stationary and Mobile Phases Get link. The mobile phase here just forces the sample particles to move over the stationary phase. Separation is achieved by a different affinity for the two phases for the compounds you wish to separate.
The mobile phase propels a substance through a structure which holds the stationary phase enabling chromatographic separation to occur. Molecules are partitioned between a mobile phase and a stationary phase as a function of their relative sizes. Chromatography is a separation method where the analyte is combined within a liquid or gaseous mobile phase which is pumped through a stationary phase.
Stationary phase stays at the bottom of the paper chromatography while mobile phase is moving on the stationary phase and move on stationary phase till it gets its right place. For compounds that are highly polar typically reverse phase chromatography is utilized. A stationary phase and a mobile phase.
In column chromatography the stationary phase is long. Usually one phase is hydrophilic and the other lipophilic. The stationary phase is nonpolar and the mobile phase is polar.
The mobile phase is a chemically inert gas that serves to carry the molecules of the analyte through the heated column. Column chromatography takes time to separate the analytes. A scientist used reverse phase column.
Chemistry questions and answers. The separation is based on the differential partitioning between the mobile and the stationary phases.

What Is The Difference Between Mobile Phase And Stationary Phase Pediaa Com
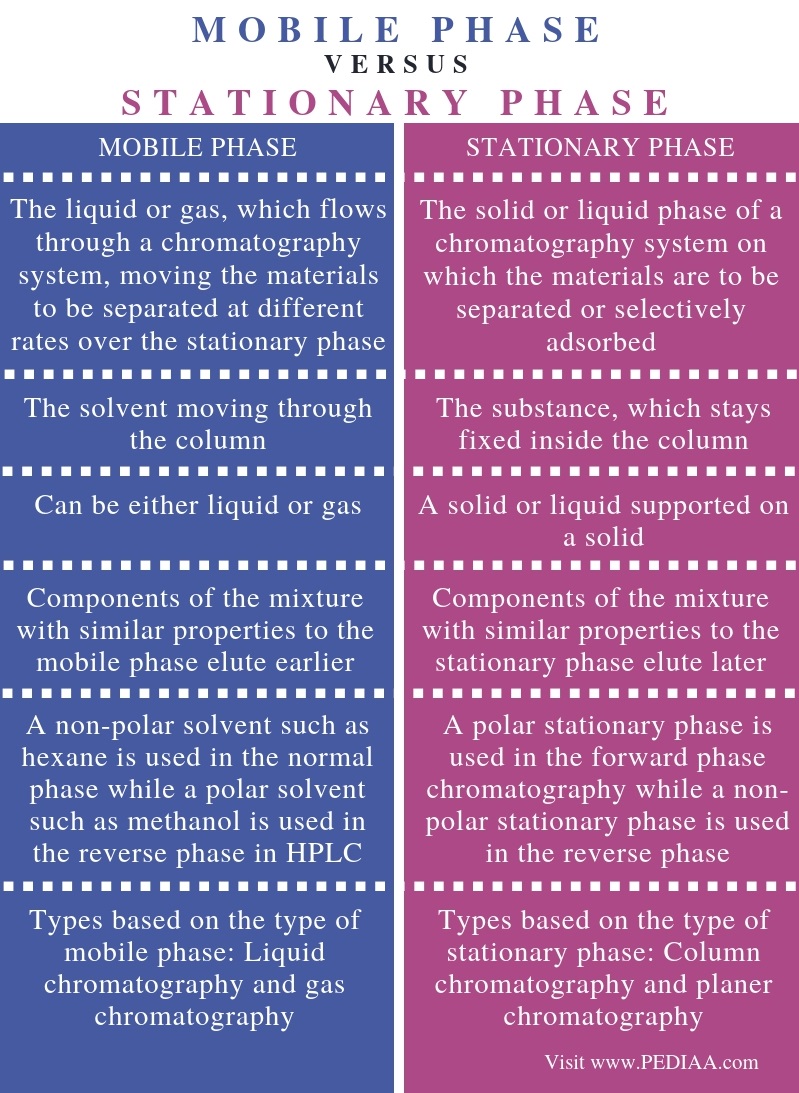
What Is The Difference Between Mobile Phase And Stationary Phase Pediaa Com

Difference Between Stationary And Mobile Phase Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms
No comments for "Explain the Differences Between Stationary and Mobile Phases"
Post a Comment